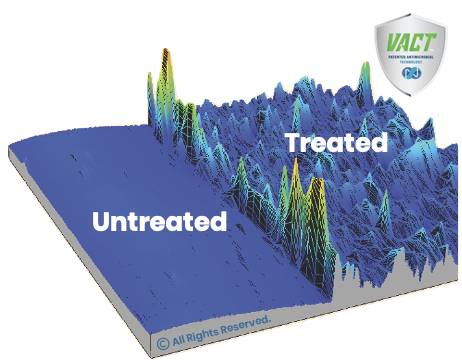
The information in this site provides a brief overview of the Nano Safe Coatings’ antimicrobial surface protection technologies based on extensive internal development and testing. Any specific antimicrobial or related claim(s) would be determined in accordance with FDA (or other regulatory authority) regulation of the device treated with the Nano Safe Coatings’ antimicrobial surface coating. This site is designed for general information for medical device manufacturers interest in the Nano Safe Antimicrobial Coatings.